KeY basics in Eclipse (Cross-project Functionality)¶
The following functionality is independent from a specific KeY-based Eclipse project.
The following sections illustrate features independent from a specific KeY-based Eclipse project using screenshots. Each section contains numbered screenshots that explain a usage scenario step by step. Clicking on each picture produces a more detailed view. The screenshots may differ from the latest release.
Create an example project¶
-
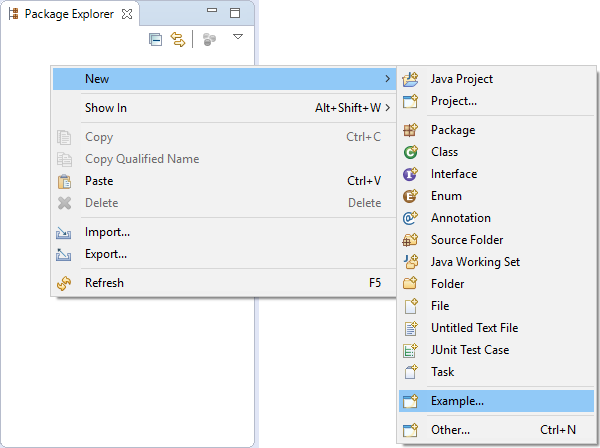
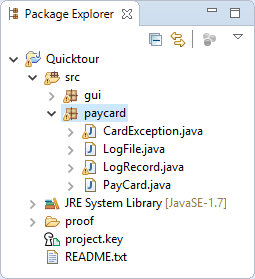
Open example project wizard via Package Explorer context menu item "New, Example...".
-
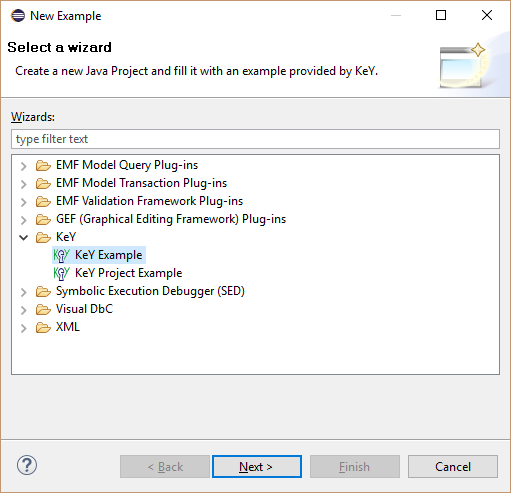
Select "KeY, KeY Example"
-
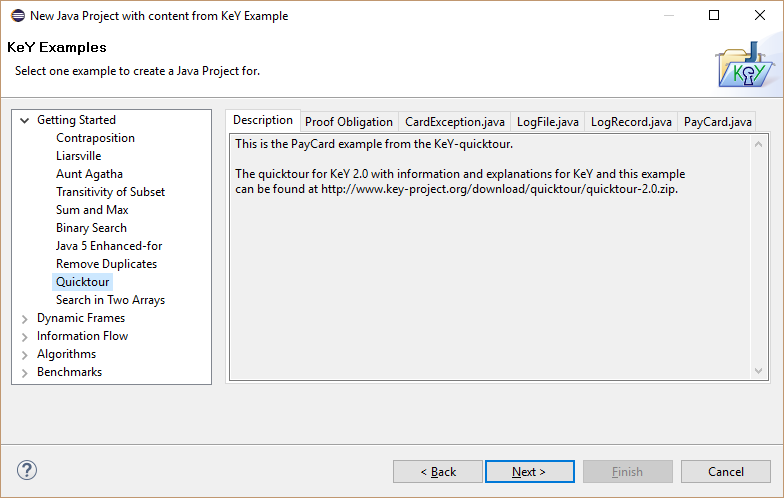
Select one of the provided examples.
-
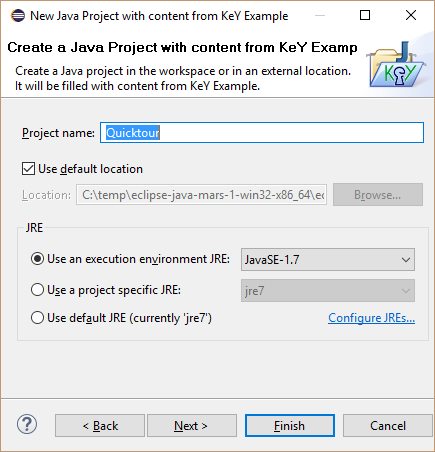
Define a project name.
-
Work with the created project. In the "Quicktour" example it is required to delete the package "gui".
Change taclet options¶
-
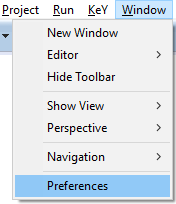
Open preference dialog via main menu item "Window, Preferences".
-
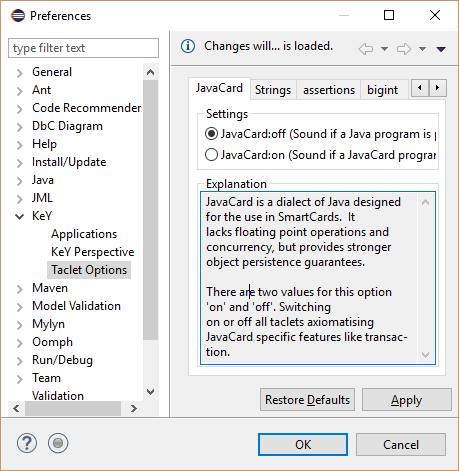
Select preference page "KeY, Taclet Options" and change settings. The next instantiate proof will use them; current proofs are not influenced by changes.
Define class path used by KeY¶
-
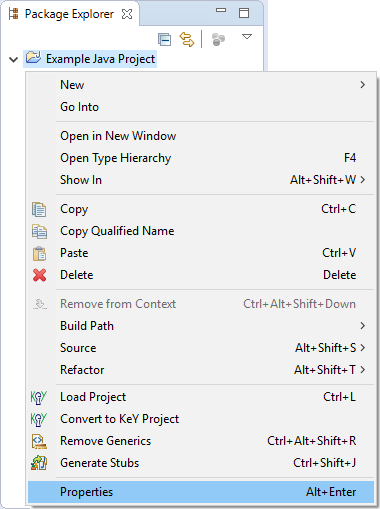
Open project properties of a Java/KeY project via context menu item "Properties".
-
Select properties page "KeY" and add additional source files. These files will be considered when the next proof is instantiated.
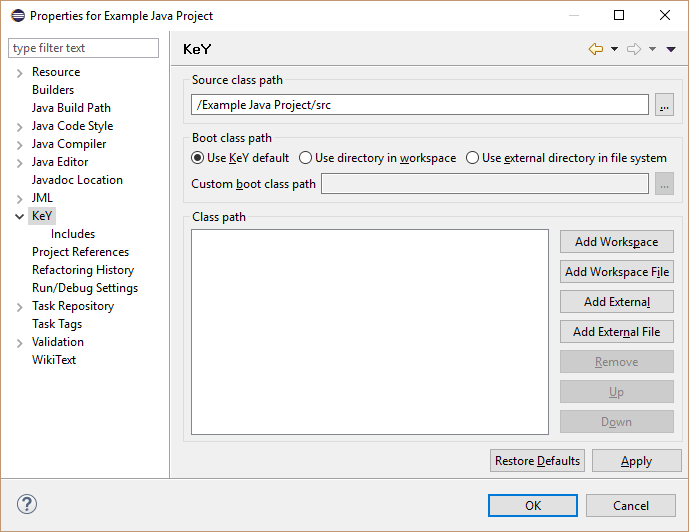
- Boot class path: Replaces stubs and specifications provided by KeY, but also method implementations are considered.
- Class path: Additional locations to the boot class path, only method stubs and specifications re considered
Troubleshooting¶
The following subsections explain solutions for common problems using KeY within Eclipse.
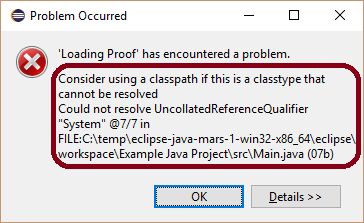
Unresolved classtype (support for API classes)¶
Problem: An error containing "Consider using a classpath if this
is a classtype that cannot be resolved" or "Could not resolve
UncollatedReferenceQualifier" is shown. The following screenshot
shows such an error message which occurred when a proof for method
magic() (see listing of Main) was started.
public class Main {
/*@ normal_behavior
@ requires System.\inv;
@ ensures \result == 42;
@*/
public static int magic() {
System.out.println(42);
return 42;
}
}
Reason: Such an error message is shown whenever KeY was unable to find a type in KeY's class paths specified in the project properties. KeY operates on source code and not on compiled byte code. This requires to provide the source code of all used types or at least stubs of called methods. Method stubs can be specified with JML. KeY itself provides such stubs and specifications only for a minimal fraction of the Java API.
Solution:
- Create a new folder, for instance named "lib_specs", within the project and ensure that the folder is not part of the regular Java class path used by JDT.
- Add the new folder to KeY's classpath (not boot class path) in the project properties as described in section Define class path used by KeY.
- Populate the folder with files "System.java" and "PrintStream.java" with content from the listings below.
Hint: Stubby can generate stub files for used API members automatically.
package java.lang;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class System {
/*@ public static invariant \invariant_for(out);
@*/
public static final PrintStream out;
}
package java.io;
public class PrintStream {
/*@ public normal_behavior
@ ensures true;
@*/
public void /*@ strictly_pure @*/ println(int x);
}